Data Modeling in Data Warehousing: Techniques, Benefits & Best Practices
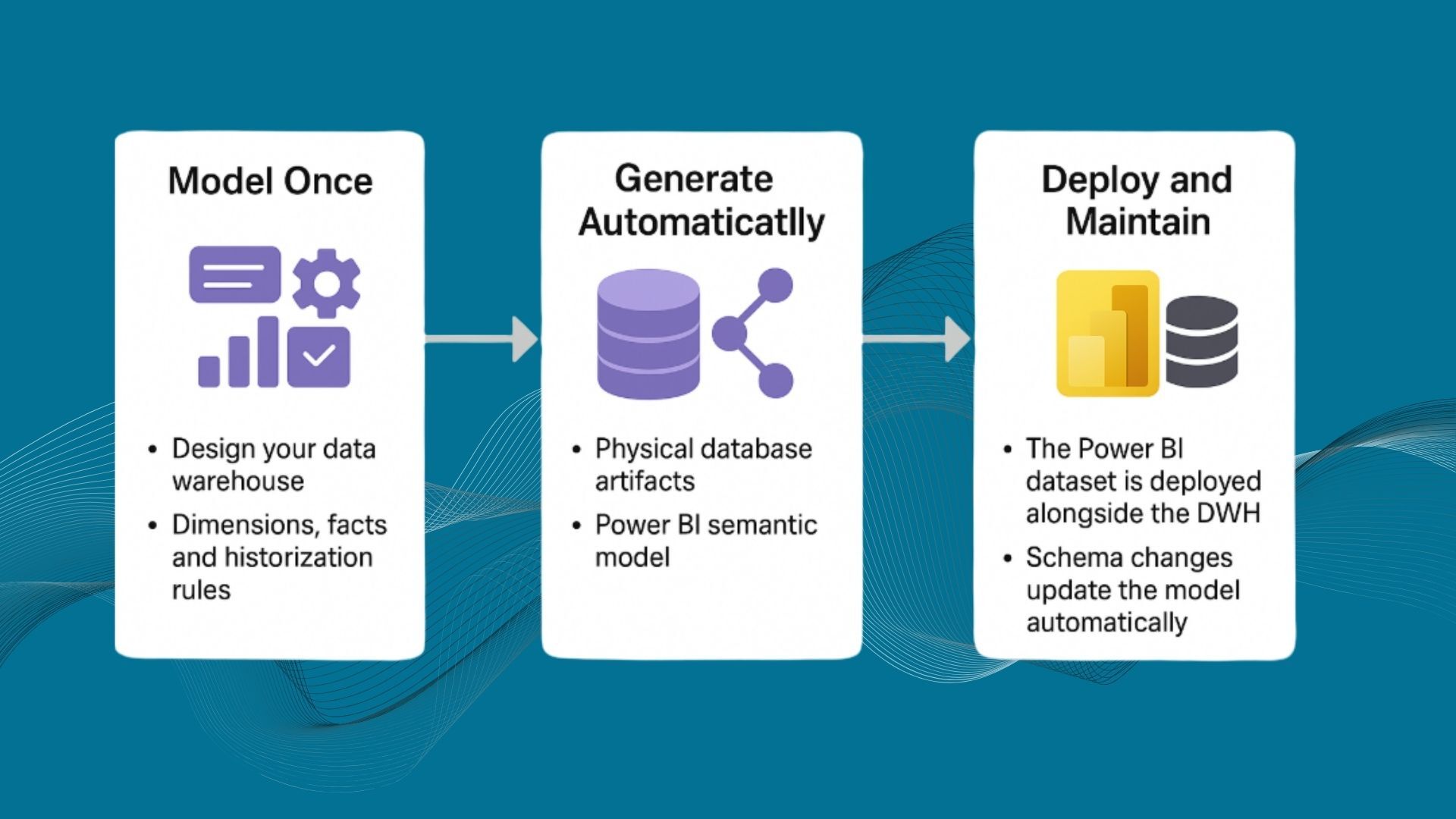
Data modeling is the foundation of every successful data warehouse. Techniques such as Inmon, Kimball, Anchor modeling, and Data Vault help you structure data so it is accurate, consistent, well organized, and easy to integrate. Good data modeling improves data quality and enables reliable reporting and analysis across the organization.
Data modeling is a critical step in the process of designing and building a data warehouse. It involves creating a conceptual and logical representation of the data that will be stored in the data warehouse. This representation helps to ensure that the data in the warehouse is accurate, consistent, and well organized.
There are several different data modeling techniques that can be used in the context of data warehousing. The four most commonly used techniques are the Inmon methodology, the Kimball methodology, Anchor modeling, and Data Vault modeling. Here is a brief overview of each technique:
- Inmon methodology: A top‑down approach centered on creating a single integrated enterprise data model from which data marts are derived.
- Kimball methodology: A business‑process‑focused approach that historically evolved bottom‑up, using fact and dimension tables to build subject‑area data marts.
- Anchor modeling: A flexible modeling technique using “anchors” (core entities) that adapt easily as business requirements change.
- Data Vault modeling: A hub‑and‑spoke architecture using hubs, links, and satellites to support scalability, auditing, and integration across complex environments.
Each of these data modeling techniques has its own set of advantages and disadvantages, and the choice depends on the organization’s needs.
Ensuring Data Accuracy
 Data modeling ensures that the data stored in the data warehouse is accurate and complete. This is achieved by identifying the relevant data sources, selecting the appropriate data elements, and defining relationships between them.
Data modeling ensures that the data stored in the data warehouse is accurate and complete. This is achieved by identifying the relevant data sources, selecting the appropriate data elements, and defining relationships between them.
Key steps to ensure data accuracy include:
- Identify relevant data sources
- Establish data quality rules
- Implement data validation checks
- Monitor data quality over time
- Involve key stakeholders
- Regularly update and maintain data
Improving Data Consistency
 Data modeling helps improve consistency by providing standardized structures, terminology, and definitions across the organization.
Data modeling helps improve consistency by providing standardized structures, terminology, and definitions across the organization.
Ways to improve data consistency include:
- Define clear data standards
- Establish strong data governance
- Implement data validation controls
- Monitor data quality regularly
- Provide training and support
- Use master data management (MDM)
Enhancing Data Organization
 Data modeling enhances data organization by creating a logical structure aligned with business processes, making data easier to retrieve, manage, and analyze.
Data modeling enhances data organization by creating a logical structure aligned with business processes, making data easier to retrieve, manage, and analyze.
- Define a data architecture
- Develop a logical data model
- Implement data governance
- Use metadata management
- Adopt a data catalog
- Ensure strong data security
Facilitating Data Integration
 Data modeling identifies relationships across sources and creates a unified business model, improving integration, reducing redundancy, and increasing consistency.
Data modeling identifies relationships across sources and creates a unified business model, improving integration, reducing redundancy, and increasing consistency.
- Define integration requirements
- Create a data integration strategy
- Use ETL or metadata‑driven automation tools
- Implement data quality checks
- Use data virtualization where appropriate
- Implement master data management (MDM)
Enabling Effective Reporting and Analysis
 With strong data modeling, analysts can quickly retrieve relevant data, trust its accuracy, and use it effectively for reporting and decision‑making.
With strong data modeling, analysts can quickly retrieve relevant data, trust its accuracy, and use it effectively for reporting and decision‑making.
- Define reporting requirements
- Develop a reporting strategy
- Use BI and reporting tools
- Implement data visualization techniques
- Enable self‑service analytics
- Ensure strong data quality
Key Takeaways
Data modeling ensures accuracy, consistency, integration, and effective reporting in modern data warehouses. Each modeling technique—Inmon, Kimball, Anchor, and Data Vault—offers unique strengths and should be chosen based on organizational needs.
Well‑designed data models improve decision‑making, reduce errors, and increase efficiency across analytics processes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is data modeling in data warehousing?
Data modeling is the process of defining how data is structured, stored, and related inside a data warehouse. It ensures accuracy, consistency, and usability.
Which data modeling method is best: Inmon, Kimball, Anchor, or Data Vault?
No single method is universally best. The right choice depends on scalability needs, business complexity, data integration strategies, and governance requirements.
Why is data modeling important for analytics?
It organizes data logically, reduces inconsistencies, and makes reporting faster and more reliable.
Can data modeling enhance data integration?
Yes. By defining relationships across sources, modeling eliminates redundant data, simplifies transformations, and enables unified analytics.
What role does metadata play in data modeling?
Metadata describes structure, lineage, and rules which helps automate integration, governance, and analytics workflows.
Does a data warehouse require one specific modeling method?
No. Many organizations mix techniques, for example, Data Vault for ingestion and Kimball for business consumption.