English
Regular transformation
Regular Transformation
A regular transformation is a VIEW generated by AnalyticsCreator based on the defined transformation parameters. Tables, table relationships, and transformation columns must be specified, after which AnalyticsCreator automatically creates the transformation VIEW.
Below is a typical regular transformation definition:
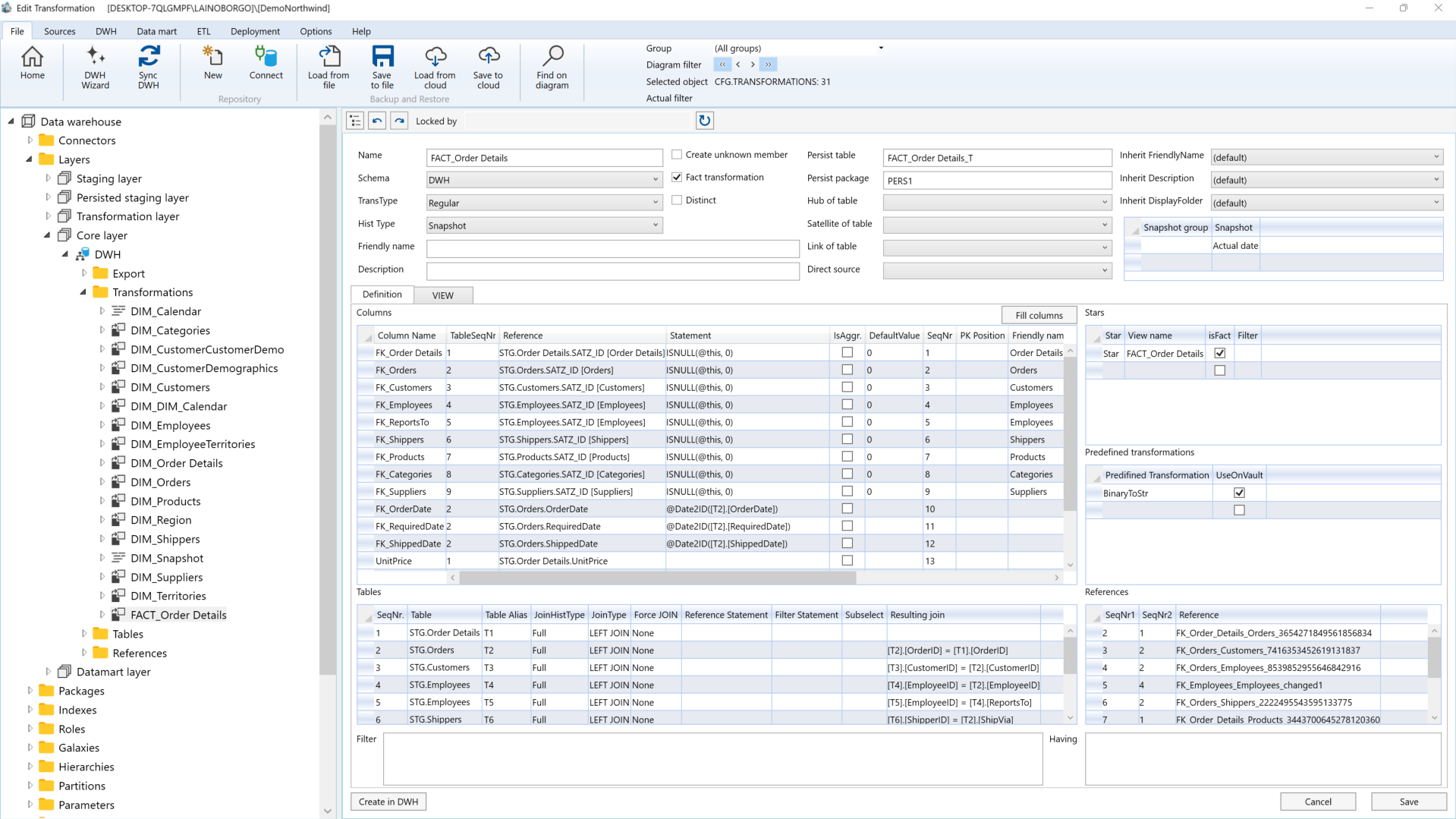 Regular transformation properties:
1. Historization type: Defines how to work with historicized data.
1. FullHist: A fully historicized transformation where the result includes specific fields. This type is commonly used for defining dimensions. Fields:
1. [SATZ_ID]
2. [DAT_VON_HIST]
3. [DAT_BIS_HIST] fields. Usually used to define dimensions.
2. SnapshotHist: Fully historicized transformation with data for predefined snapshot dates only. This type is usually used to define dimensions.
3. Snapshot: A transformation that uses predefined snapshot dates to combine historicized data. It is usually used to define facts.
4. ActualOnly: Combines historicized data, but only actual data is used. This can be used to create dimensions and facts.
5. None: Used to work with non-historicized data
2. Create unknown member: Usually used in dimensions. This option adds a new row with a surrogate ID = 0 and default values for the fields. It is used as a dimension member when the corresponding dimension member is not found during fact processing.
3. Fact transformation: This option should be selected for fact transformations.
4. Persist table: The name of the table where the transformation results will be stored.
5. Persist package: The name of the SSIS package used to persist the transformation results.
6. SSIS Package: Relevant for external or script transformations. This is the name of the SSIS package that launches the transformation.
7. Hub of table: Read-only. The source table for hub transformations.
8. Sat of table: The source table for satellite transformations.
9. Link of table: Read-only. The source table for link transformations.
10. Snapshots: A list of snapshots and snapshot groups used in the transformation. This is relevant only for historization types Snapshot and SnapshotHist.
11. Tables: A list of tables participating in the transformation.
1. SeqNr: A sequential number that should be unique for each table.
2. Table: The name of the table.
3. Table Alias: The alias of the table. It should be unique and is used in column and reference statements.
4. JoinHistType: Defines how the historical table should be joined.
1. None – The table doesn’t contain historical data.
2. Actual – Only the actual data from the historical table will be used.
3. Historical_from – The data that was valid at the start of the "guilty" period of the linked record.
4. Historical_to –The data that was valid at the end of the "guilty" period of the linked record.
5. Full – All historicizing information remains available.
5. Join type:
1. INNER JOIN
2. LEFT JOIN
3. RIGHT JOIN
4. FULL JOIN or CROSS JOIN
6. Force Join: Forces a specific join type:
1. LOOP JOIN
2. HASH JOIN
3. MERGE JOIN
7. Reference statement: Here the user can refine or redefine the reference statement used for join, for example:
Regular transformation properties:
1. Historization type: Defines how to work with historicized data.
1. FullHist: A fully historicized transformation where the result includes specific fields. This type is commonly used for defining dimensions. Fields:
1. [SATZ_ID]
2. [DAT_VON_HIST]
3. [DAT_BIS_HIST] fields. Usually used to define dimensions.
2. SnapshotHist: Fully historicized transformation with data for predefined snapshot dates only. This type is usually used to define dimensions.
3. Snapshot: A transformation that uses predefined snapshot dates to combine historicized data. It is usually used to define facts.
4. ActualOnly: Combines historicized data, but only actual data is used. This can be used to create dimensions and facts.
5. None: Used to work with non-historicized data
2. Create unknown member: Usually used in dimensions. This option adds a new row with a surrogate ID = 0 and default values for the fields. It is used as a dimension member when the corresponding dimension member is not found during fact processing.
3. Fact transformation: This option should be selected for fact transformations.
4. Persist table: The name of the table where the transformation results will be stored.
5. Persist package: The name of the SSIS package used to persist the transformation results.
6. SSIS Package: Relevant for external or script transformations. This is the name of the SSIS package that launches the transformation.
7. Hub of table: Read-only. The source table for hub transformations.
8. Sat of table: The source table for satellite transformations.
9. Link of table: Read-only. The source table for link transformations.
10. Snapshots: A list of snapshots and snapshot groups used in the transformation. This is relevant only for historization types Snapshot and SnapshotHist.
11. Tables: A list of tables participating in the transformation.
1. SeqNr: A sequential number that should be unique for each table.
2. Table: The name of the table.
3. Table Alias: The alias of the table. It should be unique and is used in column and reference statements.
4. JoinHistType: Defines how the historical table should be joined.
1. None – The table doesn’t contain historical data.
2. Actual – Only the actual data from the historical table will be used.
3. Historical_from – The data that was valid at the start of the "guilty" period of the linked record.
4. Historical_to –The data that was valid at the end of the "guilty" period of the linked record.
5. Full – All historicizing information remains available.
5. Join type:
1. INNER JOIN
2. LEFT JOIN
3. RIGHT JOIN
4. FULL JOIN or CROSS JOIN
6. Force Join: Forces a specific join type:
1. LOOP JOIN
2. HASH JOIN
3. MERGE JOIN
7. Reference statement: Here the user can refine or redefine the reference statement used for join, for example:
sql
T5.ID = T1.CustomerID
12. A filter statement: is an additional statement used alongside the reference statement. For example:
sql
T5.Country = ‘GER’
13. Sub select: A subselect statement is used in addition to the reference statement.
14. Columns: List of transformation columns
1. Column name: The name of the column.
2. TableSeqNr: Optional. The table sequence number (from the Tables section).
3. Reference: Optional. The table column from the table above.
4. Statement: Optional. The SQL statement (table aliases should be used).
5. IsAggr:This should be checked for aggregated fields.Default value: The field value for unknown members.
6. SeqNr: The column’s sequential number.
7. PK Position: The field position in the primary key (1, 2, etc.).
8. Description: A description of the field.
15. References: The table reference used to join transformation tables (see Table References).
1. SeqNr1: The sequence number of the first table.
2. SeqNr2: The sequence number of the second table.
3. Reference: The reference name.
16. Predefined transformations: A list of predefined transformations used in the transformation.
17. VIEW tab: Contains the VIEW definition. It is read-only.
Transformation Compilation and Creation
- Compile: The transformation can be compiled by pressing the "Compile" button. In this case, the transformation VIEW will be compiled, and any errors will be detected.
- Create: The transformation can be created by pressing the "Create" button. In this case, the transformation VIEW will be created in the empty DWH, and errors will be detected.
⬅ Previous Page | ➡ Next Page
Free Trial
REGISTER NOW AND ACTIVATE YOUR FREE TRIAL