Metadata-Driven Lineage in Microsoft Fabric: Automate Compliance and Governance

TL;DR: Metadata-driven lineage in Microsoft Fabric and Synapse turns compliance from a manual chore into a natural output of automation. Teams get built-in auditability, governance checkpoints, and full data flow traceability—driven by AnalyticsCreator’s automated pipelines across SQL Server, ADF, and Fabric.
Why lineage matters for compliance and audit readiness
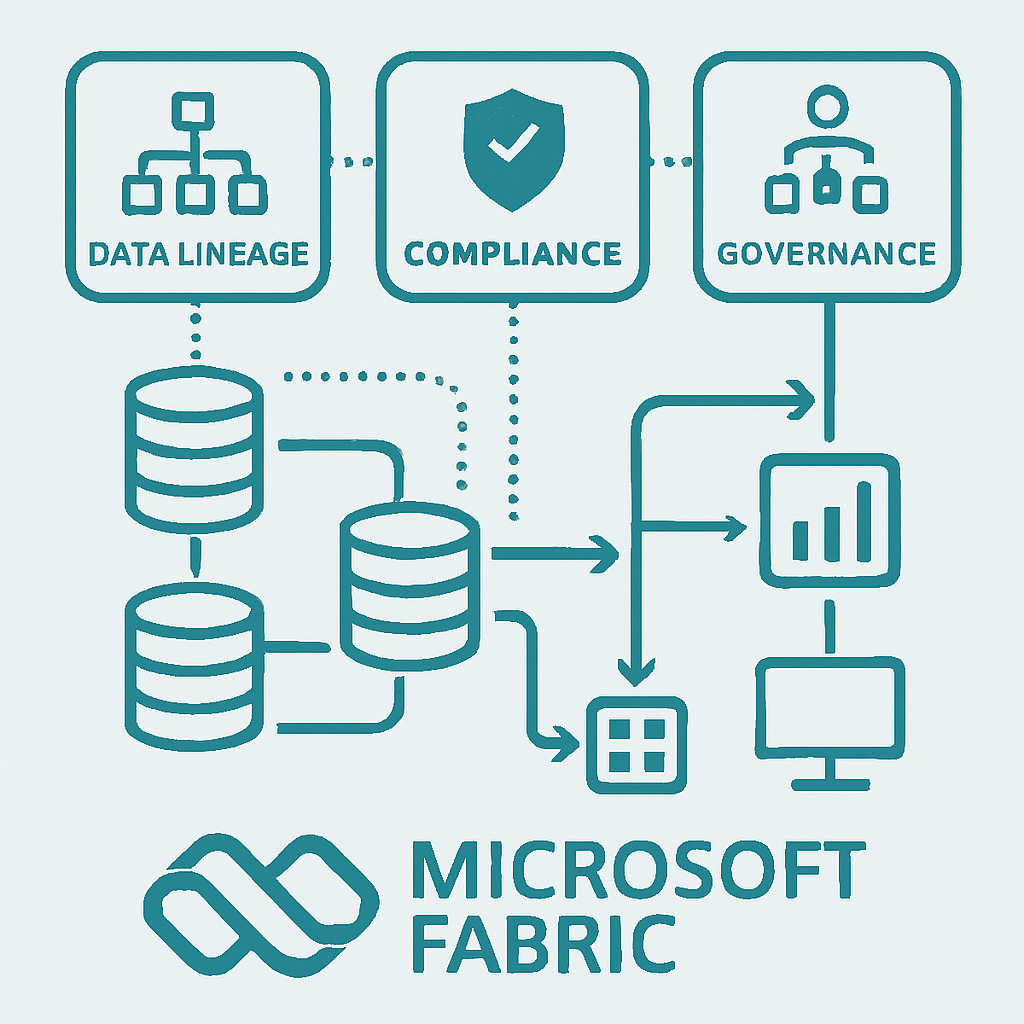
Changes to data pipelines and transformations often require compliance reviews and audit reporting. With metadata-driven lineage, every object and transformation is recorded automatically, generating visual lineage diagrams that show end-to-end flow—from source to dashboard. Auditors and governance teams gain instant access to validated data trails, improving confidence and reducing compliance overhead.
How to implement metadata-driven lineage
Using AnalyticsCreator, teams capture lineage data as part of model and pipeline generation. Metadata defines every data object, transformation, and dependency. These are centrally stored, updated with each deployment, and visualized in interactive diagrams. Microsoft Purview can layer on classification, sensitivity, and access reviews. Together, this provides full traceability across Fabric, Synapse, Power BI, and SQL-based services.
Embedding governance into the pipeline
Automation ensures every deployment updates lineage views and compliance artifacts. Changes to models, data sources, or outputs are recorded and testable. Approval workflows, change tracking, and audit triggers can be built into CI/CD pipelines. Engineers focus on delivery; governance happens in the background, continuously and consistently.
The result: continuous compliance, by design
AnalyticsCreator makes lineage and governance inherent—not optional—by design. Microsoft Fabric and Synapse pipelines are generated with lineage baked in, and governance becomes a property of the system, not a separate process. This accelerates regulatory response, improves transparency, and reduces risk across the Microsoft data stack.
Explore how AnalyticsCreator automates lineage, testing, and governance across your Microsoft environment → Book a demo
Frequently Asked Questions
What is metadata-driven lineage in Microsoft Fabric?
It’s the automatic tracking of all data flows and transformations using metadata, visualized as lineage diagrams across Fabric and Synapse.
Why is lineage important for compliance?
It provides an auditable trail of where data came from, how it was transformed, and where it’s used—critical for GDPR, SOX, and internal controls.
How does AnalyticsCreator support lineage?
It captures lineage at the metadata level during model and pipeline generation, then visualizes it automatically.
What tools integrate with metadata-driven lineage?
AnalyticsCreator works with Microsoft Fabric, Synapse, Power BI, and Purview to deliver unified lineage and governance.
Can governance checkpoints be automated?
Yes. Governance validations can be embedded into CI/CD pipelines, ensuring every deployment includes audit and compliance controls.
How is this better than manual documentation?
It’s faster, always up-to-date, and less error-prone. Manual documentation quickly becomes outdated and is hard to audit.
What are the technical requirements?
A metadata-driven platform like AnalyticsCreator and integration with Microsoft Fabric, Synapse, or SQL-based services.
Who benefits from this model?
Data engineers, compliance teams, auditors, and IT leaders all gain transparency, control, and reduced compliance risk.